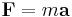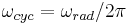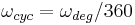Rotational speed
Rotational speed (sometimes called speed of revolution) tells how many complete rotations (i.e. revolutions or cycles) there are per time unit. It is therefore a cyclic frequency, measured in hertz (revolutions per second) in the SI System. The units revolutions per minute (rpm or 1/min) are more common in everyday life.
Rotational speed can measure, for example, how fast a motor is running. Rotational speed and angular speed are sometimes used as synonyms, but typically they are measured with a different unit. Angular speed, however, tells the change in angle per time unit, which is measured in radians per second in the SI system. Since there are 2π radians per cycle, or 360 degrees per cycle, we can convert angular speed to rotational speed by:
and
where
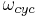 is rotational speed in cycles per second
is rotational speed in cycles per second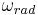 is angular speed in radians per second
is angular speed in radians per second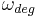 is angular speed in degrees per second
is angular speed in degrees per second
For example, a stepper motor might turn exactly one complete revolution each second. Its angular speed is 360 degrees per second (360°/s), or 2π radians per second (2π rad/s), while the rotational speed is 60 rpm.
Rotational speed is not to be confused with tangential speed, despite some relation between the two concepts. Imagine a rotating merry-go-round. No matter how close or far you stand from the axis of rotation, your rotational speed will remain constant. However, your tangential speed does not remain constant. If you stand two meters from the axis of rotation, your tangential speed will be double the amount if you were standing only one meter from the axis of rotation.